
25 hydroxyvitamin D3(25-OH-VD3)is the main form of vitamin D stored in the human body,with a half-life of up to 25 days,good stability,and high concentration.It is an active product generated by hydroxylation of vitamin D3(VD3)and can be used as an effective biomarker for clinical evaluation of human vitamin D levels.
Biological functions of 25 hydroxyvitamin D3 (25-OH-VD3)
25-OH-VD3 is an important intermediate metabolite of vitamin D. Vitamin D does not have biological activity and needs to be activated to exert its biological functions.
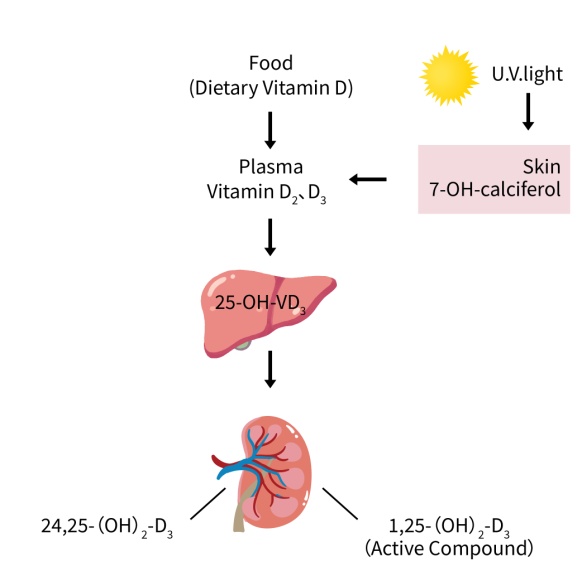
Figure 1 Activation pathway of vitamin D
As shown in Figure 1, vitamins D2 and D3 in the blood are transported to the liver by their respective binding proteins, and under the action of 25 hydroxylase, 25-OH-VD3 is generated. 25-OH-VD3 cannot directly act on tissues and needs to be transported through the bloodstream to the kidneys for further hydroxylation to form highly active 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25- (OH) 2-D3]. 1,25- (OH) 2-D3 binds to the corresponding receptor and participates in regulating calcium and phosphorus metabolism, maintaining the balance of bone minerals, and regulating the growth and differentiation of tissue cells; In addition, it also has functions such as regulating immunity, promoting cell apoptosis, and inhibiting tumor cell proliferation.
Clinical application of 25 hydroxyvitamin D3
The content of 25 hydroxyvitamin D3 (25-OH-VD3) is an effective indicator for clinical evaluation of vitamin D nutritional status. Vitamin D can ensure the normal development of the human body and maintain the normal function of the skeletal and muscular systems. Vitamin D deficiency is not only directly related to musculoskeletal disorders, but also associated with various diseases:
Vitamin D deficiency
As shown in Table 1, there are significant differences in the serum 25-OH-VD3 levels among patients with different musculoskeletal system diseases。
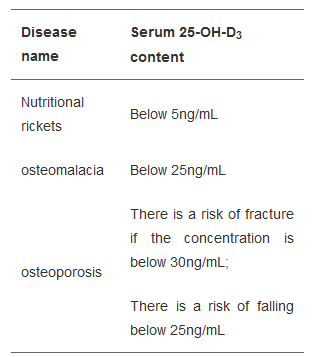
Table 1 Relationship between different musculoskeletal system diseases and 25-OH-D3 content
Metabolic syndrome
Serum VD level of metabolic syndrome is negatively correlated with the risk of metabolic syndrome (MS) such as hypertension, diabetes and obesity. Studies have shown that individuals with serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D [25- (OH) D] levels less than 15 ng/mL have higher blood sugar levels and a two-fold increased risk of hypertension compared to those with levels greater than 26 ng/mL. For every 0.29nmol/L decrease in serum 25- (OH) D levels, waist circumference increases by 1cm; for every 0.74nmol/L decrease, body mass index increases by 1kg/m2.
cardiovascular disease
When the concentration of vitamin D in the human body is lower than the optimal level, it can cause an increase in parathyroid hormone, activation of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system, increased insulin resistance, and thus lead to cardiovascular system risks. A research team conducted an eight year follow-up of cardiovascular disease patients and found that individuals with serum 25- (OH) D levels below 8ng/mL had a higher risk of cardiovascular disease mortality compared to those with levels above 28ng/mL.
malignant tumor
Vitamin D has the effect of promoting cell differentiation and inhibiting cell proliferation, and VD deficiency is associated with the occurrence of malignant tumors. Research shows that the incidence rate of colon cancer will be reduced by at least 40% when the serum 25- (OH) D content increases by 20ng/mL; If 25- (OH) D content is sufficient, women's risk of breast cancer will be significantly reduced.
infectious diseases
Vitamin D can induce endogenous immune cells to express antimicrobial peptides, thereby exerting antibacterial and antiviral effects; VD deficiency can lead to a decrease in the body's defense ability, resulting in infection.
references
[1] Zhu Jianjun, Wang Anping, Tian Kexiong, etc Biological functions and applications of vitamin D3 [J]. Feed Research, 2009, 6; 38-41
[2] Zhang Yanmei Research on the Physiological Function and Mechanism of Hydroxy-D3 [J]. Shanxi Agricultural Science, 2006, 34 (2); 76-78.
[3] Priemel M, yon Domams C,Klatte TO, et a1.Bone mineralizationdefects and vitamin D deficiency:histomorphomertic annlysis ofiliac crest bone biopsies and circulating 25-hydr0xyvitamin D in675 patients [J]. Bone Miner Res, 2010, 25; 305-312.
[4] Zhan Keqin, Zhang Yuhong, Peng Weihua, etc The clinical significance of detecting 25 hydroxyvitamin D3, parathyroid hormone, and osteocalcin in osteoporosis [J]. Experimental and Laboratory Medicine, 2013, 31 (6); 583-584.
[5] Mertens PR, Muller R. Vitamin D and candiovascular risk[J]. IntUrol Nephro1. 2010, 42; 165-171.
[6] Li Junjun, Ding Xiaochun Dynamic changes and significance of serum 25 hydroxyvitamin D3 levels in newborns [J]. Chinese Journal of Children's Health, 2012, 20 (2); 130-131.
[7] Ma Congcong, Liu Yanqin The level and clinical significance of 25 hydroxyvitamin D3 in peripheral blood of patients with non Hodgkin lymphoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Hematology, 2015, 23 (2); 431-434.
[8]Adam JS, Hewison M. Update in vitamin D [J]. Clin EndocrinolMetab, 2010, 95; 471-478.
[9] Jiang Wei, Gao Fengrong Research progress on vitamin D deficiency related diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis, 2014, 20 (3); 331-337.
[10] Mao Meng, Liu Zhen Physiological functions and clinical applications of vitamin D3 [J]. West China Medical Journal, 1991, 8 (3); 299-301.
[11] Zhou Jiansuo, Zhang Jie Progress in Clinical Application Research of Vitamin D [J]. Laboratory Medicine, 2013, 28 (6); 539-543.

 Company Address
Company AddressNo. 778 Guoyao Road, Hulan District, Harbin City, Heilongjiang Province
 Contacts
ContactsManager Ma
 Tel
Tel+86 451 5879 4677
 E-mail
E-mailchaoqunhechuang@hrbcqhc.com

